US carmaker Tesla needs lithium to power its electric vehicles, but where does the company get it from? Find out more here.
As the energy transition continues to unfold, US electric vehicle (EV) pioneer Tesla (NASDAQ:TSLA) has been making moves to secure supply of the raw materials it needs to meet its production targets.
Lithium in particular has caught the attention of CEO Elon Musk. Back in 2020, the battery metal had a spotlight moment at Tesla’s Battery Day, when Musk shared that the company had bought tenements in the US state of Nevada, and was looking for a new way to produce lithium from clay — a process yet to be proven at commercial scale.
Since then, lithium prices have hit all-time highs and, despite retreating in 2023, have stayed elevated. Prices for other key battery metals have also increased, leading to higher costs for batteries themselves. According to Benchmark Mineral Intelligence, raw materials currently make up about 80 percent of battery costs, up from around 40 percent back in 2015.
“Price of lithium has gone to insane levels,” Musk tweeted back in April 2022. “There is no shortage of the element itself, as lithium is almost everywhere on Earth, but the pace of extraction/refinement is slow.”
Most lithium mining happens in Australia from hard-rock sources and in Chile from brines. But lithium refining is dominated by China, which currently accounts for more than 75 percent of global lithium processing capacity.
“I’d like to once again urge entrepreneurs to enter the lithium-refining business. The mining is relatively easy, the refining is much harder,” Musk said during a July 2022 earnings call for Tesla, adding that there are software-like margins to be made in the lithium-processing business. “You can’t lose — it’s a license to print money.”
Do Tesla batteries have lithium and cobalt?
As mentioned, it wasn’t just lithium that saw prices climb in 2021 — cobalt doubled in price that same year, and although it has declined since then, the battery metal remains essential for EV batteries. Most cobalt mining takes place in the Democratic Republic of Congo, which is often associated with child labor and human rights abuses, fueling concerns over long-term supply.
Tesla is known for using nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA) cathodes developed by Japanese company Panasonic (OTC Pink:PCRFF,TSE:6752). This type of cathode has higher energy density and is a low-cobalt option, but has been less adopted by the industry compared to the widely used nickel-cobalt-manganese (NCM) cathodes. Aside from that, South Korea's LG Energy Solutions (KRX:373220) is working on supplying Tesla with batteries using nickel-cobalt-manganese-aluminum cathodes.
That said, not all Tesla’s batteries contain cobalt. In 2021, Tesla said that for its standard-range vehicles it would be changing to lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) cathodes, which are cobalt- and nickel-free. At the time, the company was already making vehicles with LFP chemistry at its factory in Shanghai, which supplies markets in China, the Asia-Pacific region and Europe.
In April 2023, Tesla announced that it plans to use this type of cathode chemistry for its short-range heavy electric trucks, which it calls "semi light." The company is also looking to use LFP batteries in its mid-sized vehicles.
How much lithium is in a Tesla battery?
How much lithium do Tesla batteries actually contain? For those interested in the EV space, it's a fair question to ask.
The answer is that even though it might not be a huge amount compared to other raw materials, lithium can become a hurdle for any EV maker if there’s not enough — or not enough of the right quality.
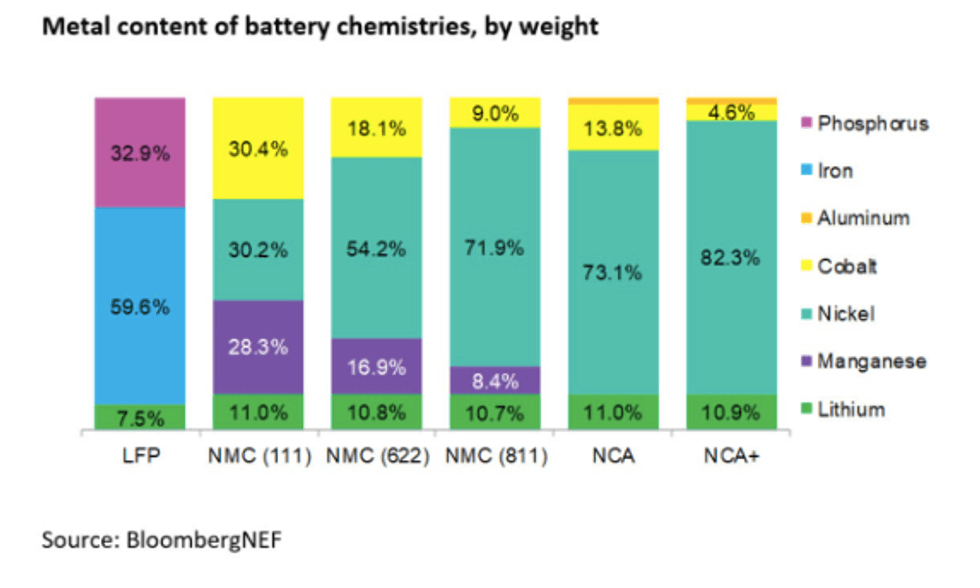
Back in 2016, Musk said batteries don't require as much lithium as they do nickel or graphite — he described lithium as "the salt in your salad" and said it is about 2 percent of the cell mass. While he underestimated that number, as you can see below, the metal still only makes up about a 10th of a given battery.
Metal content of battery chemistries by weight.
Chart via BloombergNEF.
But a key factor to remember is volume — given the amount of batteries Tesla needs to meet its ambitious goals, it could hit a bottleneck if it can’t secure a steady supply of raw materials. Of course, this is true not just for Tesla, but for every carmaker producing EVs today and setting targets for decades to come.
For that reason, demand for lithium is expected to soar in the coming years. By 2030, Benchmark Mineral Intelligence forecasts that lithium demand will reach 2.4 million metric tons (MT) of lithium carbonate equivalent — much higher than the forecast 900,000 MT of demand expected in 2023.
Which lithium companies supply Tesla?
It's important to understand that there is not only one company that supplies lithium to Tesla.
At the end of 2021, Tesla inked a fresh three year lithium supply deal with top lithium producer Ganfeng Lithium (OTC Pink:GNENF,SZSE:002460). The Chinese company will provide products to Tesla for three years starting in 2022. Major miners Livent (NYSE:LTHM) and Albemarle (NYSE:ALB) also have supply contracts in place with the EV maker, and China’s Sichuan Yahua Industrial Group (SZSE:002497) agreed to supply battery-grade lithium hydroxide to Tesla back in 2020 for a period of five years.
The company also holds deals with junior miners for production that is yet to come on stream. Liontown Resources (ASX:LTR,OTC Pink:LINRF) is set to supply Tesla with lithium spodumene concentrate from its AU$473 million Kathleen Valley project. The deal is for an initial five year period set to begin in 2024, conditional on Liontown starting commercial production by 2025.
Core Lithium (ASX:CXO,OTC Pink:CXOXF) was previously in talks with Tesla to supply the car company with lithium from its Finniss project, but negotiations collapsed in October 2022. The lithium firm remains open to further dialogue with Tesla.
In January 2023, Tesla amended its agreement with Piedmont Lithium (ASX:PLL,NASDAQ:PLL), which is now set to supply the US automaker with spodumene concentrate from the past-producing North American Lithium operation — a project Piedmont is developing with Sayona Mining (ASX:SYA,OTCQB:SYAXF). Under the amended agreement, the ASX-listed company will deliver approximately 125,000 MT of spodumene concentrate to Tesla beginning in the second half of 2023 through to the end of 2025.
Even though Tesla has secured lithium from all these companies, the EV supply chain is a bit more complex than buying lithium directly from miners. Tesla also works with battery makers, such as Panasonic and CATL (SZSE:300750), which themselves work with other chemical companies that secure their own lithium deals.
What company makes Tesla’s batteries?
Tesla is currently working with Japanese company Panasonic, its longtime partner, as well as South Korea’s LG Energy Solutions, the second largest battery supplier in the world. They supply the EV maker with cells containing nickel and cobalt.
China's CATL has been supplying LFP batteries to Tesla for cars made at its Shanghai plant since 2020. It’s also been reported that BYD Company (OTC Pink:BYDDF,SZSE:002594) is supplying Tesla with the Blade battery — a less bulky LFP battery — which the car manufacturer has used in some of its models in Europe.
Are Tesla’s batteries expensive because of lithium costs?
Battery costs have been rising on the back of inflation, price hikes for raw materials and the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war, among other factors. Raw materials, including lithium, currently make up about 80 percent of battery costs, up from around 40 percent back in 2015, according to information from Benchmark Mineral Intelligence.
Lithium prices are at historic highs, and it’s not only spot prices that are climbing — lithium producers have said contract prices are also up, with some moving from fixed to more variable agreements.
Is there enough lithium for electric cars?
There’s plenty of lithium in the Earth’s crust, but extracting, processing and qualifying it for its use in EVs is a different story. Lithium demand from the EV sector is rising, a trend that is expected to continue throughout the decade. But supply is not keeping up, with many analysts and even lithium producers forecasting a tight market ahead.
At the moment, there aren't enough raw materials in the pipeline to take the majority of EV makers beyond 2030, as per Benchmark Mineral Intelligence.
Will Tesla buy a lithium mine?
For carmakers, securing lithium supply to meet their electrification goals is becoming a challenge, which is why the question of whether they will become miners in the future continues to come up.
As mentioned, back in 2020, Musk surprised the lithium industry by saying Tesla had acquired the rights to lithium-rich clay deposits in Nevada; it said it had found a way to mine the material in a sustainable and simple way — using table salt and water.
But mining lithium is not easy, and despite speculation, it's hard to imagine an automaker being involved in it, SQM’s (NYSE:SQM) Felipe Smith said. “You have to build a learning curve — the resources are all different, there are many challenges in terms of technology — to reach a consistent quality at a reasonable cost,” he said. “So it's difficult to see that an original equipment manufacturer (OEM), which has a completely different focus, will really engage into these challenges of producing.”
Even so, OEMs are coming to the realization that they might need to build up EV supply chains from scratch after the capital markets' failure to step up, Benchmark Mineral Intelligence’s Simon Moores believes. Furthermore, automotive OEMs that are making EVs will in effect have to become miners.
“I don't mean actual miners, but they are going to have to start buying 25 percent of these mines if they want to guarantee supply — paper contracts won't be enough,” he said.
Which company is the top lithium producer?
When looking at the world's lithium producers by market cap, the top three are: US-based Albemarle, which has lithium brine operations in the US and Chile and hard-rock operations in Australia; Chile's SQM, with its main operations in the Salar de Atacama in Chile; and Chinese company Ganfeng, which has resources around the world.
Where is Tesla's lithium refinery?
Even though Tesla does not mine lithium at the moment, it recently broke ground on its Texas lithium refinery. Musk has said the facility could produce enough lithium for about 1 million EVs by 2025. The company is expecting to finish building the site by next year, reaching full production a year after. Tesla's lithium refinery capacity is yet to be announced.
This is an updated version of an article first published by the Investing News Network in 2022.
Don't forget to follow us @INN_Resource for real-time updates!
Securities Disclosure: I, Priscila Barrera, hold no direct investment interest in any company mentioned in this article.
Editorial Disclosure: The Investing News Network does not guarantee the accuracy or thoroughness of the information reported in the interviews it conducts. The opinions expressed in these interviews do not reflect the opinions of the Investing News Network and do not constitute investment advice. All readers are encouraged to perform their own due diligence.
From Your Site Articles
- Lithium Market 2023 Year-to-Date Review ›
- Lithium Market Update: Q1 2023 in Review ›
- 7 Biggest Lithium-mining Companies in 2023 ›
- 5 Things Lithium Investors Can Expect from Now Until 2025 ›
- Tesla May Get into Lithium Mining, Will Others Follow? ›
Related Articles Around the Web