What are the layer 3 routing protocols?
- Internet Protocols IPv4/v6.
- Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
- Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP)
- Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Routing operates at layer 3, where packets are sent to a specific next-hop IP address, based on destination IP address. Devices in the same layer 2 segment do not need routing to reach local peers.
Layer 3 is the network layer and its protocol is the Internet Protocol or IP. Devices in an IP network are identified by an IP address, which can be dynamically assigned and may change over time.
A router is a commonly utilised Layer 3 device. Operating at Layer 3, a router will inspect the IP and IPX addresses of incoming data packets. After determining the packet source, the router will then make routing decisions based on the enclosed destination address and quality of service specifications.
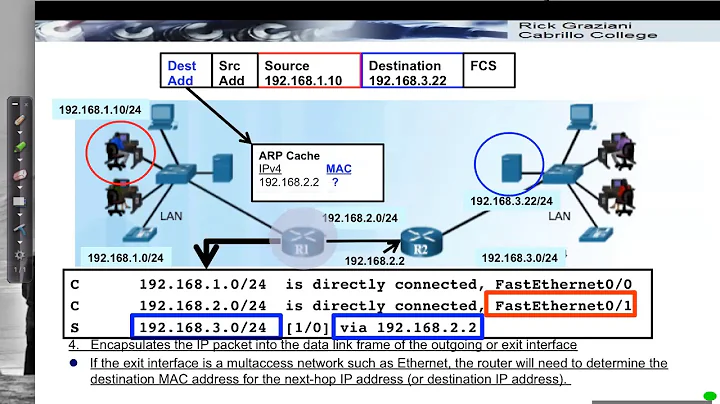
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) The Address Resolution Protocol is a layer 2 protocol used to map MAC addresses to IP addresses. All hosts on a network are located by their IP address, but NICs do not have IP addresses, they have MAC addresses. ARP is the protocol used to associate the IP address to a MAC address.
TCP and UDP are both very well-known protocols, and they exist at Layer 4. TCP favors data quality over speed, whereas UDP favors speed over data quality. Layer 3 (Network) transmits data segments between networks in the form of packets.
Layer 3 of the OSI Model: Network Layer provides the functional and procedural means of transferring variable length data sequences from a source host on one network to a destination host on a different network, while maintaining the quality of service requested by the transport layer (in contrast to the data link ...
Protocol data units of the OSI model are: The Layer 4: transport layer PDU is the segment or the datagram. The Layer 3: network layer PDU is the packet. The Layer 2: data link layer PDU is the frame.
Logical diagrams, also called layer 3 diagrams, represent the IP topology of a network. They are useful for troubleshooting routing issues, identifying potential security risks, or planning network changes. Nodes represent network devices and networks. Edges represent the connections of devices to networks.
A Layer 3 switch is both a switch and a router. So Layer 3 switch is a switch that can route traffic, and a router with multiple Ethernet ports has a switching functionality. It can switch packets by checking both IP addresses and MAC addresses.
What is Layer 3 network topology?
Layer 3 network topologies are defined as networking architectures that are composed of devices that are capable of operating at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model.
- Internetworking: This is the main duty of network layer. ...
- Addressing: Addressing is necessary to identify each device on the internet uniquely. ...
- Routing: In a network, there are multiple roots available from a source to a destination and one of them is to be chosen.
Layer 3 switches make the use of virtual local area networks (VLANs) and interVLAN routing easier and faster. They make VLANs easier to configure because a separate router isn't required between each VLAN; all the routing can be done right on the switch.
- Also, while NAT is a layer 3 (network) protocol, proxy servers usually work at layer 4 (transport, e.g. TCP proxies) or higher (e.g. http proxies) . - Working at a higher layer makes proxy servers slower than NAT devices in most cases.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 link management protocol that provides path redundancy while preventing loops in the network.
The MAC address is a layer 2 (data link) address. The layer 3 address is a logical address. It will pertain to a single protocol (such as IP, IPX, or Appletalk). The layer 2 address is a physical address.
Layer 3 is the Network or Internet layer. When transmitting data, this layer adds a header containing the source and destination IP addresses to the to the data received from the Transport layer. The packet it creates will then be forwarded to the MAC or Data Link layer.
In the OSI model, we learnt that Switches belong to Layer 2 while Routers belong to Layer 3. Switches are understood to be forward traffic based on MAC address while Routers perform the forwarding based on IP address. ]
The application layer is frequently referred to as layer 3. It is a layer that hosts decentralized networks applications (DApps) and the protocols that allow them. While certain blockchains, including Ethereum or Solana (SOL), support a robust ecosystem of Layer three applications, Bitcoin is not suited to host them.
The main difference between a Layer 2 and Layer 3 switch is the routing function. A Layer 3 switch (also called a multilayer switch) performs all the functions a Layer 2 switch does; however, it has both static and dynamic routing functions.
Is static routing a Layer 3?
Switches that add only Static Routing to their software features are considered to be somewhere between a Layer 2 and full Layer 3 switch.
In a typical, centralized Layer 3 forwarding model, a Layer 3 router (virtual and physical) receives packets from a Cisco Nexus 1000V and forwards the traffic across the segments. In this model, the Layer 3 router can become a point of congestion or blockage for the flow of traffic.
A firewall generally works at layer 3 and 4 of the OSI model. Layer 3 is the Network Layer where IP works and Layer 4 is the Transport Layer, where TCP and UDP function. Many firewalls today have advanced up the OSI layers and can even understand Layer 7 – the Application Layer.
Subnets Work on Layer 3
A subnet works at the IP layer or Layer 3 of the OSI Model. Subnets enable you to create smaller networks inside a larger overall network. A standard IPv4 address is typically broken up into a Network ID and Host ID.
- Eliminates network latency.
- Facilitates routing between virtual LANs.
- Lower broadcast traffic volumes.
- Separates routing tables and boosts segregation of traffic.
- Simplifies the configuration process for VLANs.
- Simplifies troubleshooting and identification of faults.
There are several sorts of network protocols.
Layer 2 − The second layer is the data link layer. Data link layers 2 are best shown by Mac addresses and Ethernet. Layer 3 − Layer 3 is a network layer that identifies the best available communication channel in the network. Layer 3 is exemplified by an IP address.
BGP in networking is based on TCP/IP. It operates on the OSI Transport Layer (Layer 4) to control the Network Layer (Layer 3). As described in RFC4271 and ratified in 2006, the current version of BGP-4 supports both IPv6 and Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR), which enables the continued viability of IPv4.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 link management protocol that provides path redundancy while preventing loops in the network.
TCP, UDP, and ICMP are examples of Layer 4 protocols used to provide a delivery mechanism between end stations. It is also at this layer in the model that applications will be distinguished by information in the Layer 4 headers within the packets.
L1 is a speaker's first language. L2 is the second, L3 the third etc. A learner whose L1 is Spanish may find Portuguese and Italian easy languages to learn because of a fairly close connection between the languages.
Which protocol is used in Layer 3 or 4?
The most important protocol for this process is the Internet Protocol (IP). Protocols at layer 3 do not open connections, ensure reliable data delivery, or indicate which service on the targeted device should use the data; those are layer 4 processes. Layer 4 involves the use of transport protocols like TCP and UDP.
The main difference between L1 L2 and L3 cache is that L1 cache is the fastest cache memory and L3 cache is the slowest cache memory while L2 cache is slower than L1 cache but faster than L3 cache. Cache is a fast memory in the computer. It holds frequently used data by the CPU.
- Also, while NAT is a layer 3 (network) protocol, proxy servers usually work at layer 4 (transport, e.g. TCP proxies) or higher (e.g. http proxies) . - Working at a higher layer makes proxy servers slower than NAT devices in most cases.
Telnet belongs to the OSI layer 7 (application layer) and IP belongs to the OSI layer 3 (network layer). At the network layer, the protocol is indeed connectionless, and at the application layer, it is indeed connection-oriented.
The IP address is a layer 3 (network layer) address. The MAC address is a layer 2 (data link) address. The layer 3 address is a logical address. It will pertain to a single protocol (such as IP, IPX, or Appletalk).
However, a large enterprise requires a faster, much more scalable method to provide inter-VLAN routing. Enterprise campus LANs use Layer 3 switches to provide inter-VLAN routing. Layer 3 switches use hardware-based switching to achieve higher-packet processing rates than routers.
Instead of dedicated connections between networks, VPNs use virtual connections routed (tunneled) through public networks that are typically service provider networks. Layer 3 VPN operates at the Layer 3 level of the OSI model, the Network layer.
A L3 WAN means that there's routing involved in the WAN itself. This means your next-hop will be your WAN device and not the other end of the WAN. Both ends of the WAN are in different IP subnets. Examples of L3 WAN could be MPLS L3 VPN.