Is co 3 high spin or low spin?
Co(III) complexes have a d6 valence electron configuration and are typically low-spin (S = 0) and exhibit a saturated octahedral coordination geometry. As a result, only a few cases of intermediate-spin (S = 1) or high-spin (S = 2) ground states, or observable spin-crossover, have been reported.
Strong-field ligands, such as CN− and CO, increase the Δ splitting and are more likely to be low-spin. Weak-field ligands, such as I− and Br− cause a smaller Δ splitting and are more likely to be high-spin.
Another method to determine the spin of a complex is to look at its field strength and the wavelength of color it absorbs. If the field is strong, it will have few unpaired electrons and thus low spin. If the field is weak, it will have more unpaired electrons and thus high spin.
So, for example, Co(III) is nearly always low-spin except in [CoF6]3−.
The low energy splitting of a compound occurs when the energy required to pair two electrons is lower than the energy required to place an electron in a low energy state. Usually, square planar coordination complexes are low spin complexes.
CO is a dative, L-type ligand that does not affect the oxidation state of the metal center upon binding, but does increase the total electron count by two units.
The only common high-spin cobalt(III) complex is [CoF6]3−.
3 The High-Spin (HS) Co2+ (S = 3/2) Cases. Structural and magnetic properties of transition-metal complexes of pyridine N-oxide, including cobalt(II) ions in octahedral surroundings have been reviewed by Carlin and De Jongh [36].
[Fe(CN)6]−3 is low spin complex but [Fe(H2O)6]+3 is high spin complex.
Examples of low-spin d6 complexes are [Cr(CN)6]3− and Cr(CO)6 , and examples of high-spin d6 complexes are [CrCl6]3− and Cr(H2O)6 .
Is cobalt high spin?
Among the 3d transition metal ions, cobalt is outstanding because of its spin state degree of freedom. Apart from the high-spin (HS) and low-spin (LS) states, an intermediate spin state (IS) is also proposed in many cobalt compounds.
Cobalt (59Co) is a high sensitivity nucleus with a 100% natural abundance that yields somewhat broad lines even in symmetric environments and very broad lines for slightly larger complexes over an extremely wide chemical shift range. Co is a spin 7/2 nucleus and is therefore quadrupolar.
This is because CO3+ has more tendency to form coordination complexes than Co2+.
Only complex [Cr(gly)3] is a high spin complex because it contains a weak field ligand and these type of ligands can not pair up the unpaired electrons while in other options there are atleast one strong field ligand.
Hexafluorocobaltate(III) ion is found to be high spin complex, the hybrid state of cobalt in it, is sp3d2.
CO is a ligand that has vacant pi orbitals that creates a large extent of splitting in the d orbitals of the metal atom, this makes them a strong ligand.
CO forms a coordination bond that has both sigma and pi properties. A non-bonding orbital on the CO will form the primary bond, and an anti-bonding orbital forms a bond as well. Because of this multiple coordination bond, the carbonyl-metal bond is very strong, and the energy splitting is very high.
(D) $CO$ is also neutral ligand.
Therefore, manganese will form both a high and low spin complex.
Carbon donor ligands are strong ligands and usually forms low spin complexes.
Which ligands form high spin complexes?
Weak field ligands cannot cause forcible pairing of electrons within d-subshell and thus form high spin complexes.
Co(III) complexes have a d6 valence electron configuration and are typically low-spin (S = 0) and exhibit a saturated octahedral coordination geometry.
We know Co3+ is more stable in complex compounds than Co2+ is in the same.
25 The fact that the value of U is larger for Co3+ than for Co2+ is due to the stronger on-site repulsion in the more contracted d orbitals of ions with higher oxidation state.
High spin-complex- is the complex which possesses a greater number of unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals of the central metal atom and it will be paramagnetic in nature.
More the number of electron, more the magnetic moment. Thus Fe2+ has the highest value of the magnetic moment among the given elements.
Usually outer orbital complexes (sp3d26) are high spin (or spin-free) complexes.
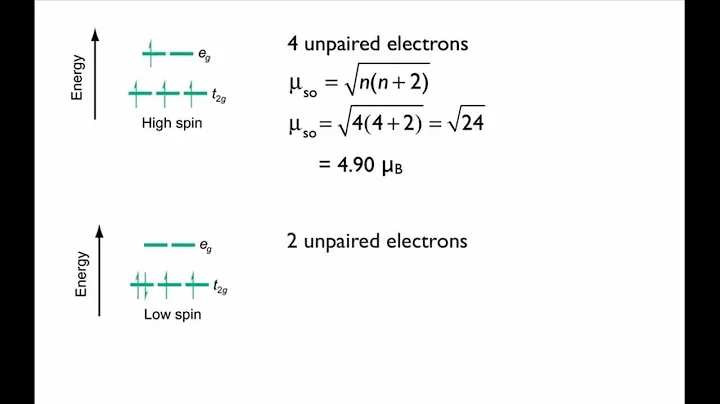
[CoF6]3− is a high spin complex and contains 4 unpaired electrons.
- We know that for high spin, d4=t32ge1g. CFSE=(–0.4x+0.6y) Δo. where, x= Number of electrons occupying t2g orbitals. y= Number of electrons occupying eg orbitals. ∴CFSE=(–0.4×3+0.6×1) Δo. =(–1.2+0.6) Δo=–0.6 Δo. ...
- ∴CFSE=(–0.4×3+0.6×1) Δo. =(–1.2+0.6) Δo=–0.6 Δo. Suggest Corrections. Similar questions. Q.
Solution: Since K4[O8(CN)6],[Mo(CO)6] has no unpaired electrons they are diamagnetic and low spin while [Mn(CN)6]4− has one unpaired electron they are paramagnetic in nature and have high spin.
What is the electron configuration of Co3+?
The electron configuration of Co3+ is [Ar]4s3d5 . Co is in Period 4 of the Periodic Table, and Ar is the preceding noble gas.
Cobalt is a lustrous very hard silvery metal belonging to a group called the "transition metals". It is one of only 3 ferromagnetic transition elements along with iron and nickel.
Grades above 0.2 per cent are average and grades of 0.3 per cent and above are considered very good, especially with scale. Grades of over 1.5 per cent copper and 2 per cent nickel are considered high grade.
Adding the two half reaction, EMF comes out to +ve. This means that Co(III) in aqueous solution has the tendency to change to Co(II). Hence, Co (III) is not stable in aqueous solution.
Cobalt (III) ion has greater tendencr to form complexes than cobalt (II) ion. Therefore, Co (II) ion, being stable in aqueous solution, changes to Co (III) ion, in the presence of complexing reagents and gets oxidised.
Outer electronic configuration of CO 3+is 3d 64s 0. Now Co in CO 3+state is not stable in aqueous solution. But Co is stable inCO 2+state in water. This is the reason it likes to go from Co(III) to Co(II) state by gaining electrons or in other words, it gets reduced and acts as good oxidizing agent.
High Spin and Low Spin
The complexion with the greater number of unpaired electrons is known as the high spin complex, the low spin complex contains the lesser number of unpaired electrons. High spin complexes are expected with weak field ligands whereas the crystal field splitting energy is small Δ.
d 6 Tetrahedral = high spin complex = t 2 g 3 eg 3. CFSE = − 3 5 × 3 + 2 5 × 3 Δ t = − 0.6 Δ t.
When a bidentate or a polydentate ligand contains donor atoms positioned in such a way that when they coordinate with the central mental ion, a 5- or 6- membered ring is formed, the effect is known as the chelate effect.
There is one more important distinction that makes second and third row transition metals low spin. In addition, the pairing energy is lower in these metals because the orbitals are larger. There is more room for two electrons in one orbital, with less repulsion.
Is d4 high spin or low spin?
In d4 low spin octahedral complex two unpaired electrons are present.
Cobalt(III) complexes of macrocyclic polyimines have been patented for use as anti-inflammatory agents, due to their superoxide coordination chemistry which is, in effect, antioxidant behavior. New solid state materials are a major research target.
Hence, C o 3 + is paramagnetic.
For Co3+ ion, BM is 0, that is no unpair of electrons in it.
Clearly cyanide is a weaker 3eld ligand than CO in iron(II) porphyrinates.
CO is a π - acid ligand. It accept electron from metal to its vacant π∗ orbital. CO is a stronger ligand than CN−
STATEMENT-1: CO is stronger ligand than CN− STATEMENT-2: CO and CN− both show synergic bonding with metal . STATEMENT-3: COandN2 are isoelectronic ligands but N2 is a weaker ligand than CO but stronger than NH3 .
It is because CO can form σ (sigma) as well as π-bond, therefore it is stronger ligand than Cl−.
CO forms a coordination bond that has both sigma and pi properties. A non-bonding orbital on the CO will form the primary bond, and an anti-bonding orbital forms a bond as well. Because of this multiple coordination bond, the carbonyl-metal bond is very strong, and the energy splitting is very high.
It has to do with the energies of the frontier orbitals. As you rightly said, both species are isoelectronic, and the orbital energies in CO are lower than those in CN−. The lower hom*o energy means that CO is a poorer σ donor orbital towards the metal than CN−. Likewise the lower LUMO makes it a better π acceptor.
Which is the strongest ligand CO or NH3?
As NH3 cannot from π bonds by back bonding, therefore, CO is a stronger ligand than NH3.
CO is a stronger Complexing reagent than NH3 because of back bonding. In case of CO, It is a good Sigma donor and a pi acceptor. There exists a back bonding in CO complexes which are a donation of electrons from the filled d orbital of metals to a pi molecular orbital of CO.
(D) $CO$ is also neutral ligand.
1 Answers. CO2+ ions can be easily oxidised to CO3+ ions because the crystal field stabilisation energy of Ci3+ ions with a d6 configuration is higher than d7 configuration.
The increasing field strength of ligands to form coordination compounds is SCN − < F − < C 2 O 2 - 4 < CN − .
Hence, CN− is the strong field ligand.
The carbon and oxygen atoms are separated by 112.8 pm, indicating the presence of a triple bond. CO has the strongest chemical bond observed, with a bond dissociation energy of 1072 kJ/mol. CO has three resonance configurations.
As we can see from the spectrochemical series CN− is a stronger ligand and will cause more splitting and so crystal field splitting will be highest in K3[Co(CN)6].
Because the π* orbitals in CO are empty and those in NO are singly occupied, these ligands interact more strongly with Fe2+ than does O2, in which the π* orbitals of the neutral ligand are doubly occupied.