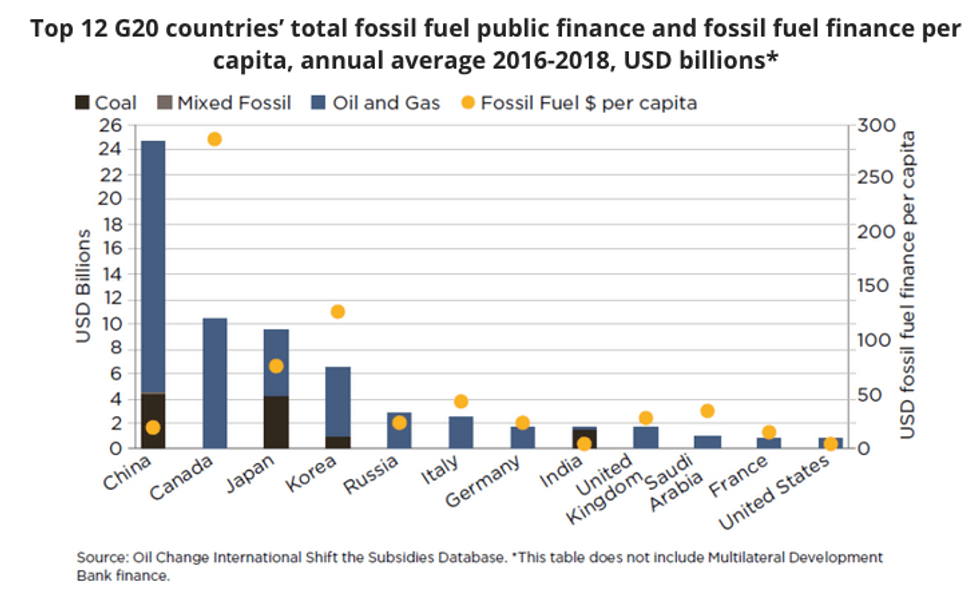
We released a report today on G20 countries' public finance for energy with Friends of the Earth U.S. that we started writing well before the world was in a global pandemic. Since then, the stakes for public finance have become a lot higher and this means the results of our research feel even more grim.
The new report looks at the trends in G20 countries' public finance for energy from 2016 to 2018--it's an update of previous research that looked at the same thing for 2013 to 2015. The headline finding is that from 2016 to 2018 G20 countries provided an average of USD 77 billion per year in public finance for fossil fuels. In 2013 to 2015, after our first report, this number was....USD 76 billion per year. G20 public finance for renewable energy also did not shift the way we need it to: from 2013 to 2015, it was USD 21 billion per year, and it rose to a still-paltry USD 24 billion per year for 2016 to 2018.
This means that right after the mostly-rich and powerful G2O countries signed the Paris Agreement with the goal of limiting global warming to 1.5oC, they went home and continued with the business-as-usual public finance policies that directly undermined this goal. Now, four years later, we are quickly running out of time to avoid the worst of the climate crisis, and we are faced with a global pandemic that is rapidly deepening other existing inequalities too.
Given the world's largest commercial banks are financing almost USD 700 billion a year for oil, gas, and coal, USD 77 billion in public finance for fossil fuels may not immediately sound like a big deal. But this public finance has an outsized influence and right now it's locking us into decades of fossil fuel infrastructure we can't afford. As G20 governments prepare historic levels of public finance in response to COVID-19 we need them to break from the past and make sure this money goes to a just and sustainable recovery instead.
Why public finance matters
There are three key reasons why the way we distribute public money for energy determines whether or not we'll succeed in building a just world with a livable climate:
1. There is a lot of it. The G20 export credit agencies (ECAs), development finance institutions (DFIs), and the multilateral development banks (MDBs) we were able to track in our new report are still only a small fraction of all public finance for energy. Worldwide, 693 public banks own assets worth USD 38 trillion, and there is an overall estimated USD 73 trillion in public finance assets when central banks, sovereign wealth funds, pensions, and multilateral banks are also included. This also does not include direct subsidies through fiscal and tax measures that governments provide -- for the G20 this support for fossil fuels is estimated at USD 80 billion a year.
2. It drives private investment. When public finance institutions invest in a fossil fuel project, this "crowds-in" private finance as well. This happens in a few different ways. First, most public finance is given at concessional rates via longer rates of return, lower interest rates, and grant components. This means it effectively acts as a subsidy and makes it a more attractive investment for others. Even when not concessional, public finance institutions help de-risk projects for private finance both through their reputation and the fact that their money is government-backed. Considering fossil fuel projects are increasingly challenged by the public for their impacts on Indigenous rights, climate, and local environmental health, this can be make-or-break. Two especially egregious recent examples of public finance institutions helping risky, contested projects go forward are Export Development Canada's backing of the Coastal GasLink pipeline and U.S. Export-Import Bank's support for Total's Mozambique LNG. Outside of bolstering individual projects, public finance institutions also send broader market signals about what kinds of energy their governments are prioritizing. Many public finance institutions have greater capacities and expertise to evaluate projects than their private counterparts. This helps build investor confidence in the projects and sectors they finance and contributes to norms in the broader financial sector.
3. It has the potential to support a just transition: As government-owned entities, public finance institutions should act in the public interest, including by tackling the climate crisis and ensuring a just transition to clean energy. These institutions do not always act in the public interest--as our report plainly shows--but there are much stronger mechanisms to force them to do so than for private finance actors. Public finance institutions could use the below-market rates, higher risk appetite, longer rates of return, and grant capacity they are currently using to boost fossil fuels to spur the creation of a fairer green economy instead. This is something many people, organizations, and coalitions mobilizing for Green New Deal, Just Transition, and Just Recovery initiatives are working hard to make governments leverage. But public finance institutions will be unable to play this role they are uniquely suited to if billions of their capital continues to flow to fossil fuels every year.
The fight for a Just Recovery
The stakes for public finance have become a lot higher in the past few months. With the health and livelihoods of billions at immediate risk from COVID-19, governments around the world are preparing public spending packages of a magnitude they previously deemed unthinkable. The fossil fuel sector and their proponents have been quick to opportunistically respond to this moment with requests for massive bailouts, new subsidies, regulatory rollbacks, and the postponement of climate measures. The Minister of Energy in Alberta, Canada has even gone as far as to call it a "great time" to build pipelines because protests to stop them cannot happen.
In some jurisdictions the fossil fuel industry is already winning many of its demands. The CARES Act in the United States could provide up to USD 471 billion to help fossil fuel companies pay off debts. Public outcry likely helped lessen the magnitude of fossil fuel bailouts initially proposed in Canada, but early support in response to COVID-19 included a USD 5.3 billion investment in and loan guarantee to the Keystone XL oil pipeline from the Government of Alberta, USD 1.9 billion in aid for abandoned well clean-up and methane leaks without fixing the regulatory gaps that allow polluters to shirk these responsibilities, a multi-billion credit facility for small and medium oil and gas producers through Export Development Canada (EDC), and other public finance programs accessible to oil and gas producers through EDC and the Canadian Development Investment Corporation.
But outside of fossil fuel industry lobby groups, the overwhelmingcallfromcivilsociety has been for governments to support a transition from fossil fuels that protects workers, communities, and the climate in order to build a more just and resilient future instead.
These efforts have highlighted the need for wealthy government responses to take international equity into account; they must ensure that debt-free public finance and debt forgiveness are extended to low income countries and communities to support a Just Recovery to this crisis. In a briefing entitled Resilient Societies or Fossil Fuel Bailouts, Oil Change detailed how governments can address the oil and gas sector in the wake of the COVID-19 crisis in ways that leave us more resilient--including through public finance measures like ending fossil fuel support, financing of Green New Deal packages, support for worker protections, and bringing the fossil fuel industry into public ownership with the explicit goal of a just and managed phase-out of production.
Just Recovery organizing is building off of and coalescing with what was already a red-hot movement to cut off new finance for fossil fuels--public and private alike--before the pandemic. And some governments and public finance institutions are responding to COVID-19 in ways that step in the direction these efforts pushing. Spain has mandated their State and public institutions divest from any holdings in companies whose activities include the extraction, refining and processing of fossil fuels (alongside other promising measures from a wealth tax to an end to any new licenses for oil and gas). The New Zealand Climate Change Commission submitted recommendations for recovery that called for stimulus investments for recovery to avoid high-emissions assets and infrastructure and to invest in education and retraining to prepare workers for low-carbon jobs. Among other measures, the European Investment Bank has established a USD 27 billion guarantee fund to support the EU's wider stimulus efforts and an additional USD 5.7 billion for recovery outside of the EU, with the Bank's president saying these measures will support climate goals.
Fossil fuel CEOs and their politician and billionaire friends are doing their best to profit from this moment. We have a long way to go until these measures add up to something resembling the Just Recovery we need for an equitable, livable, and resilient future. But from massive coalitions to creative socially-distanced rallies to radical mutual aid work, the movement is quickly gaining a foothold.